The reason why copper cables are twisted as pairs, is because the twisting of two wires would help contain the electromagnetic field that would be created as a result of electrical signals passing through the wires. Frequency characteristics of the twisted wire can limit the actual speed of data passing through a twisted pair. When the cable has a higher frequency characteristic, it means that the wire is able to contain the electromagnetic fields at higher frequency rates allowing higher speeds.
One way to increase frequency characteristics is to have more twists, more twists provides higher frequency characteristics. Another way to increase frequency characteristics is by using individually shielded pairs.
As technology advances the demand for increased data speeds will continue to grow and manufacturers will continue to develop twisted pair cables that can support those higher speeds.
CCA (Copper Clad Aluminium) vs Pure Copper CAT6 Cables
All TIA CAT6 Specs and ratings are based on Pure Copper (100% Copper) CAT6 Cable. Copper Clad Aluminium (CCA) cable and AWG (American Wire Gauge ratings) on the other hand entertains huge price discrepancies due to the fact that the aluminium cores are merely plated with copper as opposed to being pure copper and some manufacturers uses a less than minimum wire spec on cable core diameter to save on costs. For CCA CAT6 Cable, it makes for an attractive price proposition and cable performance are almost the same as full copper on shorter lengths up to around 60 meter for 0.57mm / 23AWG CAT6 CCA Cable hence why 90% of the market prefers to have CCA CAT6 Installed for home networking and POE security equipment.
First of all, copper is stronger than aluminium. This means that copper can handle higher pull tensions when installing, so there is less chance of damaging it. The aluminium in CCA has higher voltage resistance which means Power over Ethernet or PoE will be negatively affected on very long distances > 50 meter. If you choose CCA cable, make sure that you are using a power supply with enough voltage to accommodate the extra loss in power over long distances.
HCCA (High Quality CCA) is a custom spec developed to be close to Pure Copper performance and will provide POE equipment support > 100 Meters and 1Gbps Networking up to 100 Meter distances on STP CAT6A Spec Cables.
Here are the current Category standards for twisted pair cables:
- CAT 3 – 1 MHz, 10 Mbps
- CAT 5/5e – 100 MHz, 100 Mbps
- CAT 6 – 250 MHz, 1 Gbps
- CAT 6a (CAT6 Advanced, recognized TIA Standard) – 500Mhz min, 600Mhz max, up to 10 Gbps
- CAT 6e (CAT6 Enhanced, NOT a recognized TIA Standard) – 500Mhz Min, 550Mhz Max, up to 10 Gbps
- CAT 7 – 600 MHz, 10 Gbps
- CAT 7a – 1000 MHz, 10 Gbps+
- CAT 8 – 2000MHz, minimum spec 25Gbps, max 40Gbps
Variants of CAT6 / CAT7 / CAT8 Cables
Networking CAT Cable has various properties which can be applied to any category cable. CAT Cables can have any of the properties below:
- Unshielded Twisted pair (UTP) or Foiled Twisted Pair (FTP) or STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) or SFTP (Shielded & Foiled Twisted pair) or SSTP (Screened Shielded Twisted pair)
- Outdoor UV Protected Cable (Normally Black Cable) or Indoor cables (Grey, Yellow, Blue, Green etc colors)
- CCA (Copper Clad Aluminium) or Pure Copper (100% Copper) or HCCA (High Quality CCA constructed using high copper ratio than on CCA)
- Stranded or Solid Cores – Solid core cables allows longer transmission distances to be reached vs stranded core cables. Solid core also has better properties to transmit voltages for POE (Power over Ethernet) Equipment. Stranded cables can bend slightly better than solid core cables but the stranded cable are not used anymore in most installations and solid core can bend >90 degrees.
- AWG (American Wire Gauge Rating) – Millimeters per individual Core ranging from 0.51mm for CAT5 up to 0.63mm for CAT8

What Is Cat6 Cable?
Cat6 cable is otherwise called “Category 6” Ethernet cable. It consists of four pairs of copper wire which supports up to 10 Gbps of Ethernet connection. Normally, it supports a maximum transmission speed up to 1 Gbps within 100m. While Cat6 cable supports 37-55 meters (depending on crosstalk) when transmitting at a speed of 10 Gbps. It can transmit signals up to 250 MHz in frequency, which indicates how often the signal can pass through the cable. What’s more, it uses the RJ-45 standard connector and is backward compatible with its previous versions such as Cat5 and Cat5e.
AWG (American Wire Gauge) is the standard used for all electrical cables width / thickness of cable core. Poor CAT6 cable will be 0.51mm / 24 AWG Spec and will not perform well over longer distances even though it is branded as CAT6 Cables. Do NOT be Fooled by cheap spec CAT6 cable which is less than 0.55mm / 23AWG core. The industry standard is 23 AWG / 0.55mm for CAT6 as a minimum up to 0.62mm / 22 AWG. Wider cores are better (Lower AWG, Higher mm width) due to less signal attenuation on wider core cables but cable construction may be more difficult if incorrect RJ45 Connectors used. Please use wider sleeve CAT6 RJ45 connectors or CAT6 Connectors with inserts when working with wider core, lower AWG rated cables.
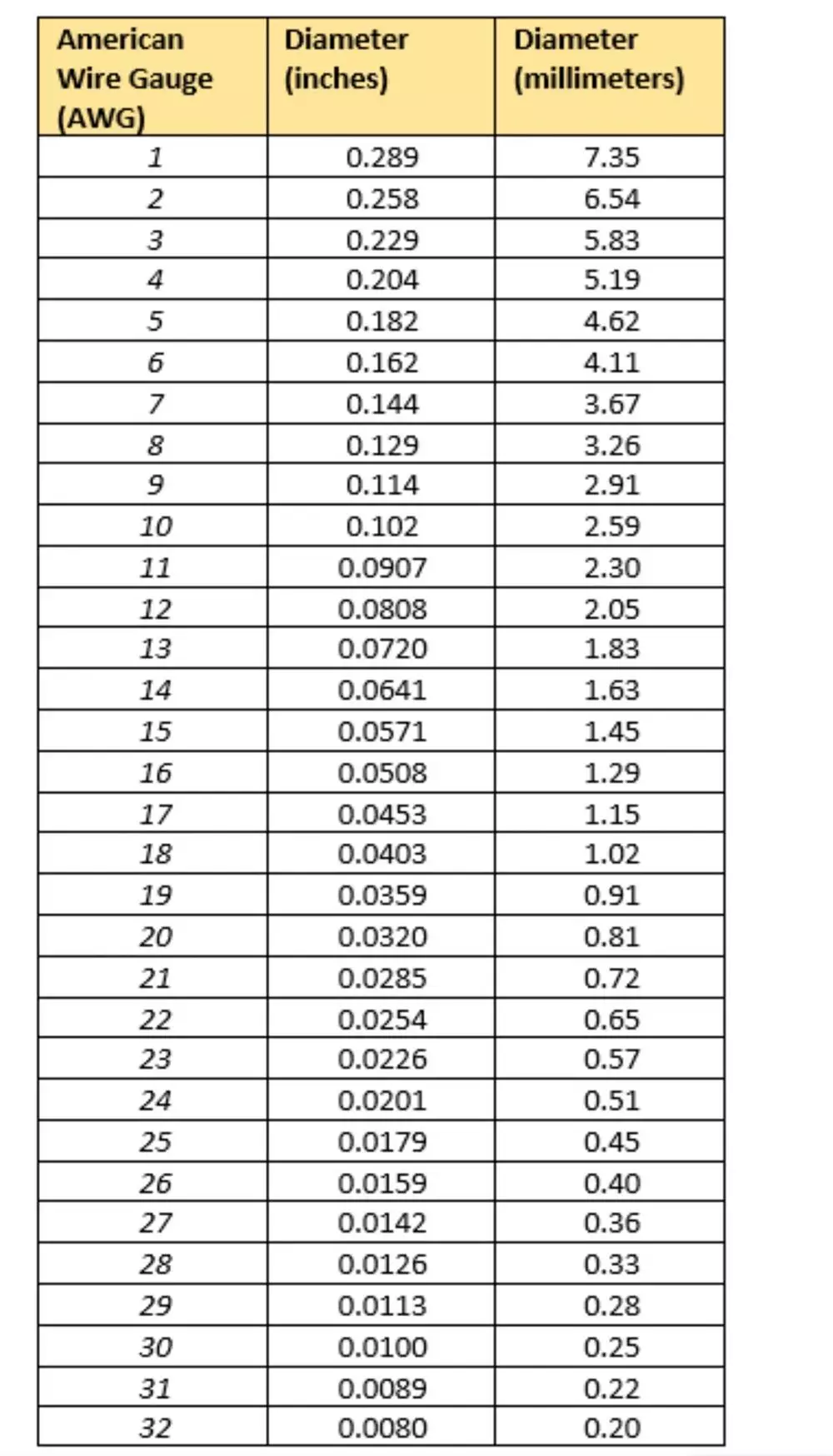
| Category | AWG | Industry Minimum (mm) | HDCabling (mm) |
| CAT6 | 23 AWG | 0.546 | 0.57 |
| CAT6a | 23 AWG | 0.546 | 0.59 |

Some products we sell for CAT6 Network Cables below
100 Meter Cable Roll | CAT6 UTP CCA Unshielded 23AWG Gigabit Network Cable
305 Meter Roll CAT6 FTP CCA Gigabit Outdoor Ethernet Cable | Black | UV Protected
The Connectors below are recommended for lower AWG (wider core) CAT6A / CAT7 / CAT8 and Outdoor / FTP or STP Cables:
CAT7 RJ45 Shielded Connector + Insert 22-24AWG Cable up to 0.62mm Conductor
Shielded eZ RJ45 CAT6/CAT7 Network Connector | Push Through Crimp with Loadbar and External Ground
CAT 7 RJ45 Network Cable Connector – Tool Free Shielded 22-26AWG Modular RJ45 Connector
What Is Cat7 Cable?
Cat7 cable is otherwise called “Category 7” Ethernet cable. It supports high-speed Ethernet communication up to 10 Gbps. The Cat7 cable is backward compatible with Cat6, Cat5 and Cat5e cable categories. It offers a 100-meter 4-connector channel using shielded cabling, and has been designed to transmit signals at a frequency of 600 MHz.
Cat 7 cables require twisted wires to be fully shielded known as screen shielded twisted pair (SSTP) or screened foiled twisted pair (SFTP) wiring, which completely eliminates alien crosstalk while significantly improving noise resistance. Thus it allows the user to get higher possible speeds even with longer cables.

What is Cat8 Cable ?
Category 8 cabling infrastructure has been designed to support short-distance (between 5 and 30 meters) runs of 25- or 40-Gbit/sec transmission and supports a frequency of up to 2 GHz (2000 MHz). While Cat8 cable requires shielded cabling as well. Most importantly, Cat8 Ethernet patch cables can support a minimum speed of 25 Gbps and even up to 40 Gbps. The physical appearance of Cat8 cable is similar to lower category cables and it can be terminated in RJ45 connections or non-RJ45 connections. Cat8 cable is also backward compatible with its previous versions. Therefore, there is no problem to use it with standard Cat7 connector.
As the IEEE continues to work toward its 25GBase-T and 40GBase-T specifications, the TIA’s Category 8 cabling specs to support those applications are now final. But this significant milestone is not by any means the proverbial end of the line for Category 8 cabling. The next wave of development will be products coming onto the market. We will continue our efforts to stay in close touch with the industry’s suppliers and bring you news of Category 8 component and system introductions.

The Connectors below can be used for CAT8 Cables
RJ45 Modular CAT7 / CAT8 Connector | Shielded | Tool Free up to 8mm Diameter Cable
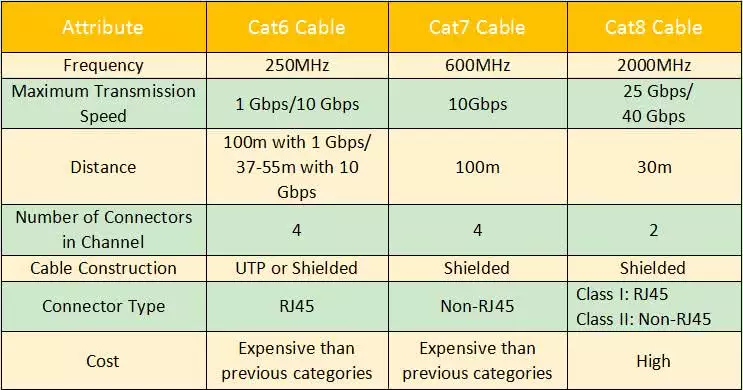
Cat6 vs Cat7 vs Cat8 Cable Comparison
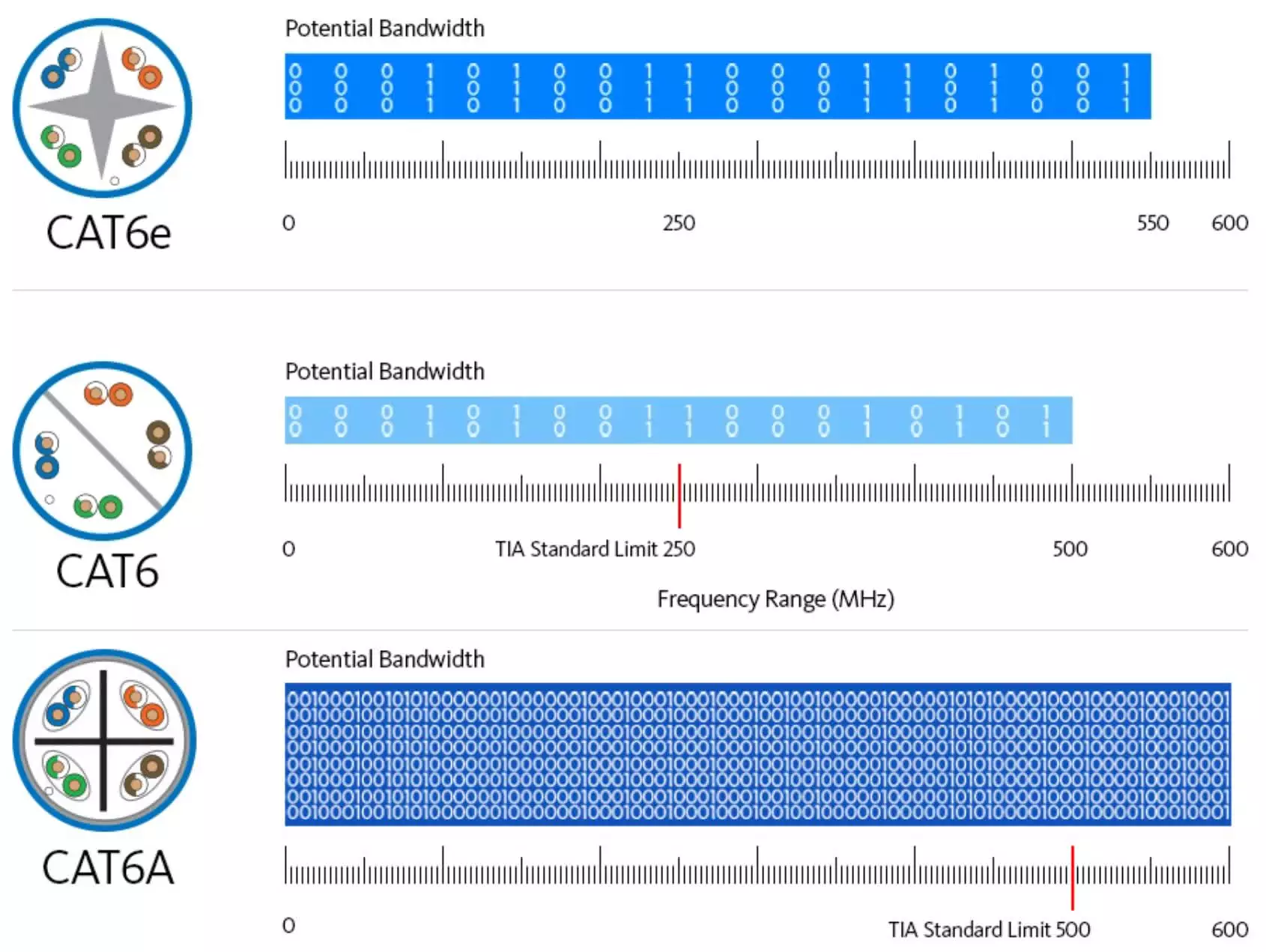
CAT6 vs CAT6A vs CAT6E
CAT6
TIA’s CAT6 standard sets the bar for CAT6 cables and connectivity. The data transmission must perform above the TIA limit for up to 250MHz. The cable can extend up to 100 meters and transfer data at a maximum data rate of 1Gbps (1000-BASE-T).
CAT6A
Another version of the CAT6 standard is available; it is labeled as CAT6A and is considered an advancement of CAT6 and almost 100% on par with CAT7 Cabling performance. TIA set the lower limit at 500MHz, which is double the CAT6 standard. The CAT6A cable can extend up to 100 meters and transfer data at a maximum data rate of 10Gbps (10GBASE-T).
CAT6e
CAT6e is not an actual standard. It has not been implemented or qualified by the TIA or any other reputable organization or commission. CAT6e is incomparable to CAT6 because the standard technically does not exist. A correct comparison would be between CAT6 and CAT6A. CAT6 is the original version, while CAT6A is the advanced version.
Although CAT6e is not technically a recognized standard, some manufacturers still manufacture products labeled with the CAT6e classification. For their purposes, CAT6e means CAT6 “enhanced”. It indicates enhancements of the original CAT6 specification that exceed the TIA limit. Typically, CAT6e claims to: double transmission frequency from 250MHz to 500MHz or even 550MHz; be equipped with a grounded foil shielding that helps data transmission reach up to 10 Gigabit Ethernet; and extend to a maximum length of 100 meters.
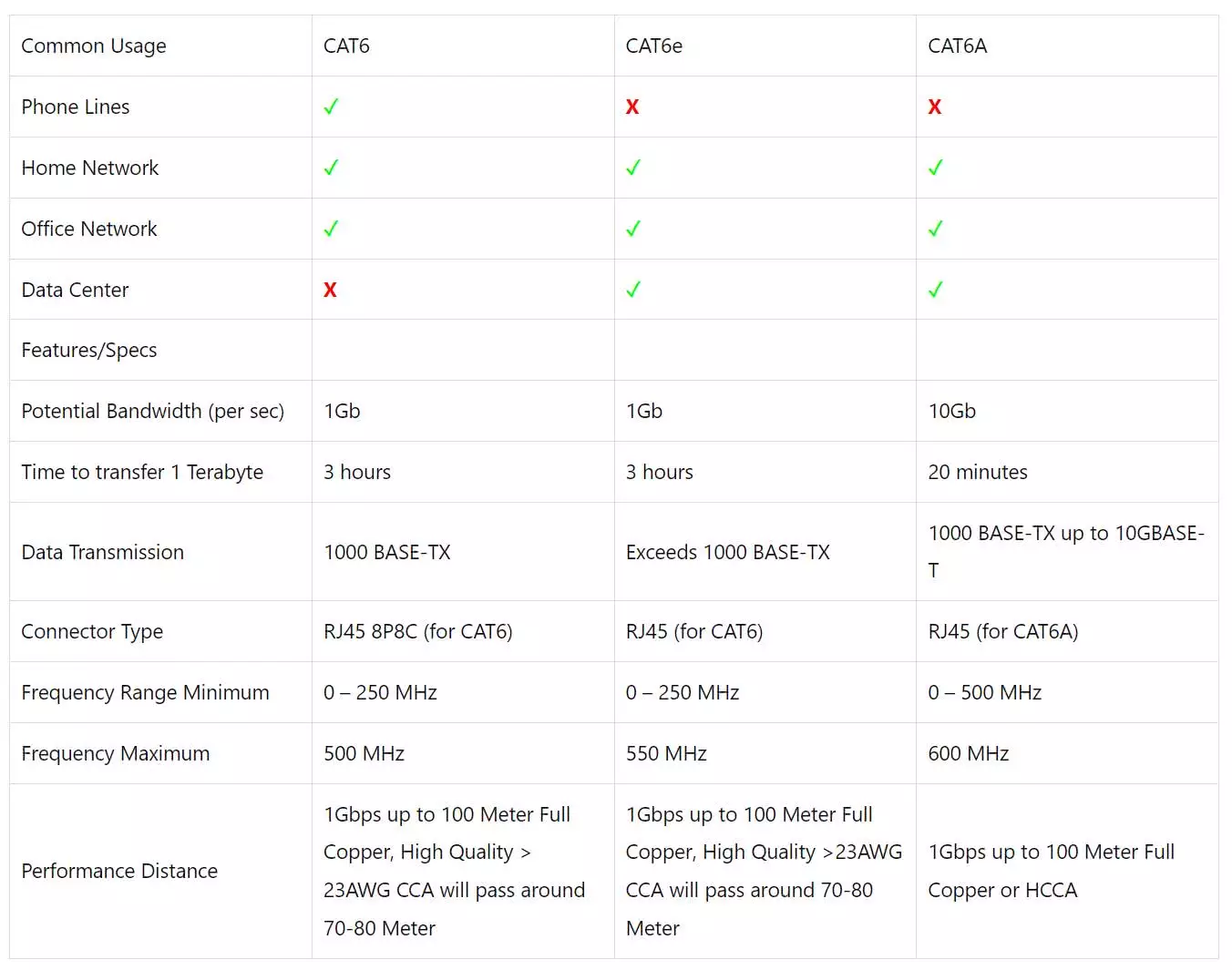
Cat6 vs Cat7
On Cat6 vs Cat7 comparison, transmission frequency and cabling length are two important factors for one to consider. From the introduction above, Cat6 cable offers the performance of up to 250 MHz while Cat7 cable is rated for transmission frequency of up to 600 MHz. The maximum cabling length of Cat6 network cable is 100m with 1 Gbps while Cat7 of 100 m with 10 Gbps.
As for cable price of Cat6 vs Cat7, Cat7 cable is more expensive than Cat6 cable if they are compared under the same conditions. If you cannot afford both of them, and then Cat5e would also be a good choice for 10G network.
By the way, the durability differs as well on Cat6 vs. Cat7. Cat6 cable has an estimated life cycle of around 10 years while Cat7 cable of around 15 years.
Cat7 vs Cat8
On Cat7 vs Cat8 comparison, transmission frequency and cabling length are also of great importance. Cat7 cable offers the performance of up to 600 MHz while Cat8 cable up to 2000 MHz. The maximum cabling length of Cat7 network cable is 100m with 10 Gbps while Cat8 of 30m with 25 Gbps or 40 Gbps.
As for cable price of Cat7 vs Cat8, Cat8 cable is more expensive for its unique feature different from the previous Ethernet cables.
Summary on Cat6 vs Cat7 vs Cat8
Last but not least, you can understand more clearly about the categories of the three Ethernet patch cables through the following table.
Information on article by https://www.fiberopticshare.com and https://infinity-cable-products.com