USB 1.1 vs USB 2.0 vs USB 3.0,3.1, 3.2 Gen1/Gen2 vs USB 4.0 | USB C vs Thunderbolt 3 vs Thunderbolt 4 Specifications
The USB Specification has been released in 1996 and has since progressed to one of the fastest interfaces on a Personal Computer.
Important!!! Most cables are wired and wire gauge is spec’d to provide fast or adaptive or supercharge charging rate on smartphones. These cables are mostly USB 2.0 Wired and manufacturers save money by not connecting all required USB 3.0 Wires if cable to be used for charging only which is both a benefit to consumer and retailer to enable lower pricing of cable for supercharge / fast charge cables. These cables will have a max data transfer speed of around 42Mbps when data copied from external solid state drives.
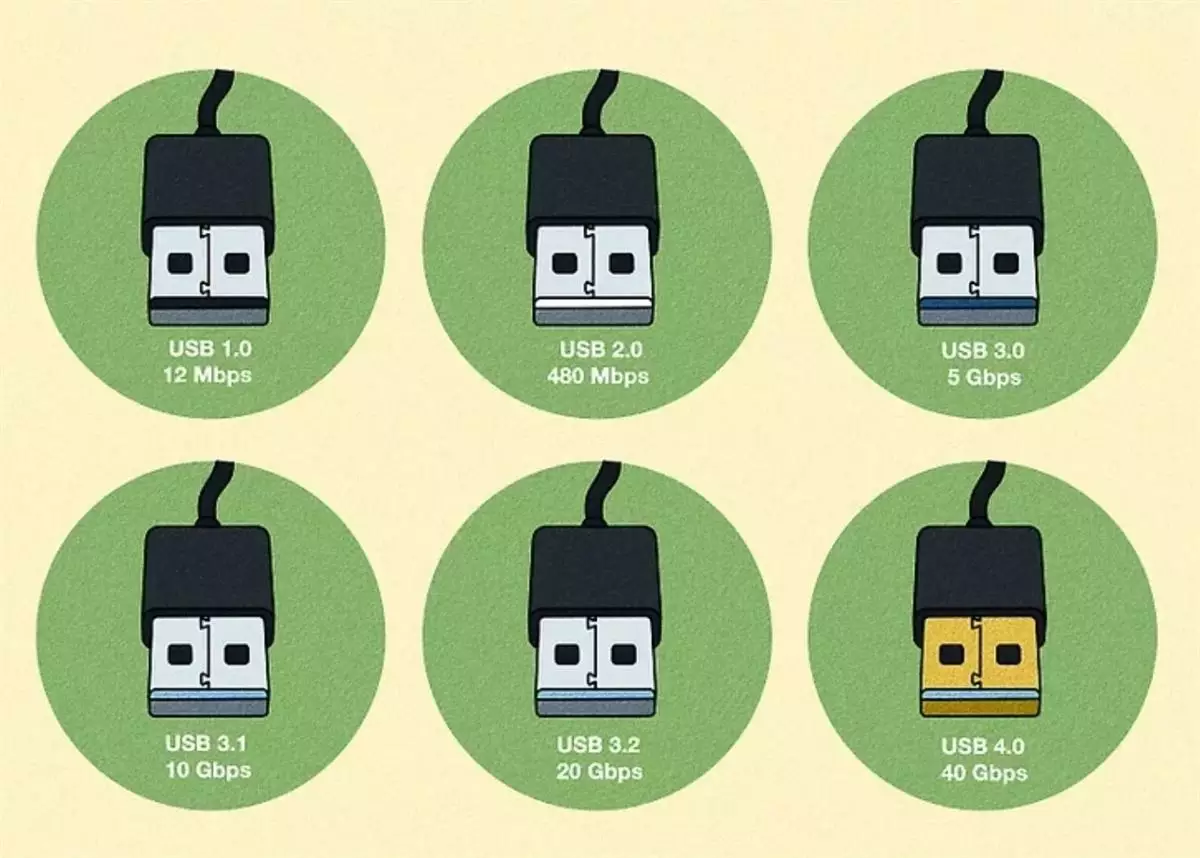
- USB 2.0 cables are the first Hi Speed USB cables –> 480Mbit/s is USB 2.0 Bus speed –> Bits to bytes = 480/8 = 60Mbps without parity overheads and error checking. In reality with overheads average is around 42Mbps data transfer speeds.
- USB 3.0 is SuperSpeed, and USB 3.1 and 3.2 are SuperSpeed+ (SuperSpeed Plus).
- Most cables have colored tabs inside the connectors that denote speed. Black is Hi Speed, blue is SuperSpeed, and teal and red are SuperSpeed+.
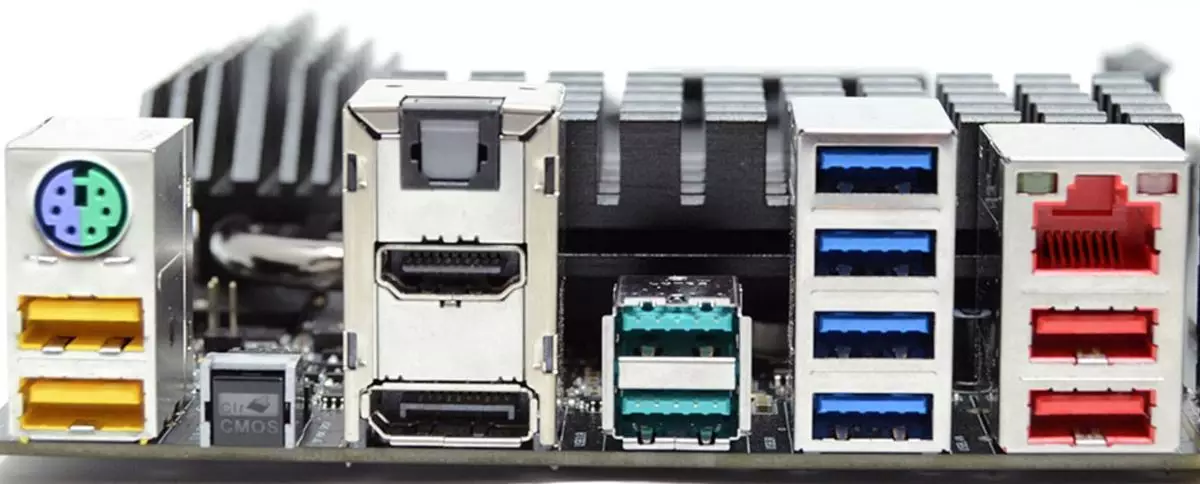
PC / Laptop Motherboard Color Coding and USB Port Layouts and Speeds:
Below are the color coding for USB Versions and Speeds on PC Motherboards or Laptops USB Ports (In general all Manufacturers must use this color coding)
- Orange/Yellow USB Ports are mostly on Smartphone Fast or Supercharge Chargers and indicates USB PD(Power Delivery) which is a compliant specification for fast / supercharge / adaptive charge smartphone charging rates.
- Red USB Connectors allows for speeds up to 20 Gbps, nearly 4 times faster than standard USB 3.0 speed of up to 5 Gbps.
- Purple USB Connectors Type-A or USB-C Indicates Huawei SuperCharge Cables / Connectors
Computer and other equipment USB ports supply 5V of electricity with a maximum current of 0.5A. This amount of current is standard across the majority of computers and means the overall power output will be 2.5 Watts at best. PD (Power Delivery) Chargers and Ports such as Yellow / Orange and USB C PD Ports can provide higher wattages above 100 Watts in some cases. PD Ports can also auto-switch voltages for charging between e.g. 5 Volt and 9 Volt or whichever voltage is optimized for the smartphone to charge.
Example PC Motherboard:
- FOUR USB 3.2 Gen 1 ports (5Gbps) in Blue
- TWO USB 3.1 ports (10Gbps) in Teal Color, all are type-A ports. This board has NO USB Type C Ports.
- TWO Yellow/Orange USB Ports – High Current Ports / Charge Port PD Power Delivery for Wireless Keyboard & Mouse or Smartphone charging
- TWO Red USB 2.0 Ports (20Gbps) – High Speeds up to 20Gbps
Micro-USB Charging and Data Cables Differences:
There are 2 different wiring methods on Micro-USB 4-pin and 4-pin USB 1.1/USB2.0 Type A cables:
- Charging cables: can only charge your smartphone and other devices but cannot transfer data. These are commonly called “Charge-only” cables.
- Data cables: does both; charges your devices and transfer data but uses more wires e.g more costly to manufacturer.
How (and why) are these cables different?
What differentiates a charge-only USB cable from a data cable is the how they are produced. More precisely, their wiring system — the number of wires within the cable. The number of wires a cable has will determine if charges your phone, transfers data, or does both.
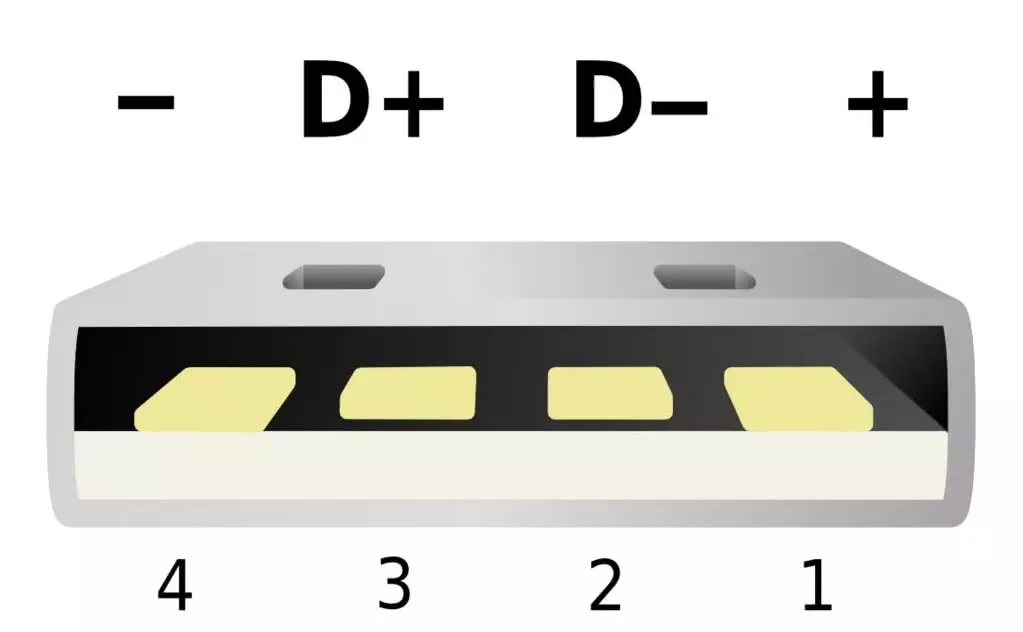
Data cables typically contain four wires (positive, negative, data transfer & data receive). The positive (+) and negative (-) wires carry electric power to the device while the other two data transfer (D+) and data receive (D-) wires are responsible for data exchange. Charge-only cables, on the other hand, only have the positive and negative power wires but lack the data exchange wires.
All USB cables have the positive and negative wires (because they are the most important) but not all USB cables have the data exchange wires — this is why some cables only charges your smartphone and cannot transfer data.
USB C Cables and Ports the applicable labeling is stated on the Cable or port:
- USB C with USB Port Logo | USB 2.0 | 480Mbit/s – Most Fast Charging / Supercharge or Adaptive Smartphone Charging Cables
- USB C SS 5 Logo | USB 3.2 Gen 1.1 | 5 Gbps
- USB C SS 10 Logo | USB 3.2 Gen 1.2 | 10 Gbps
- USB C SS 20 Logo | USB 3.2 Gen 2 | 20 Gbps | Thunderbolt 3 Enabled ONLY if carrying the Thunderbolt Logo
- USB C SS D Logo – Provides Displayport Alt Mode via Port and Cable wired to Displayport/HDMI on other end to connect a Laptop/PC from USB C to a Displayport or HDMI Display
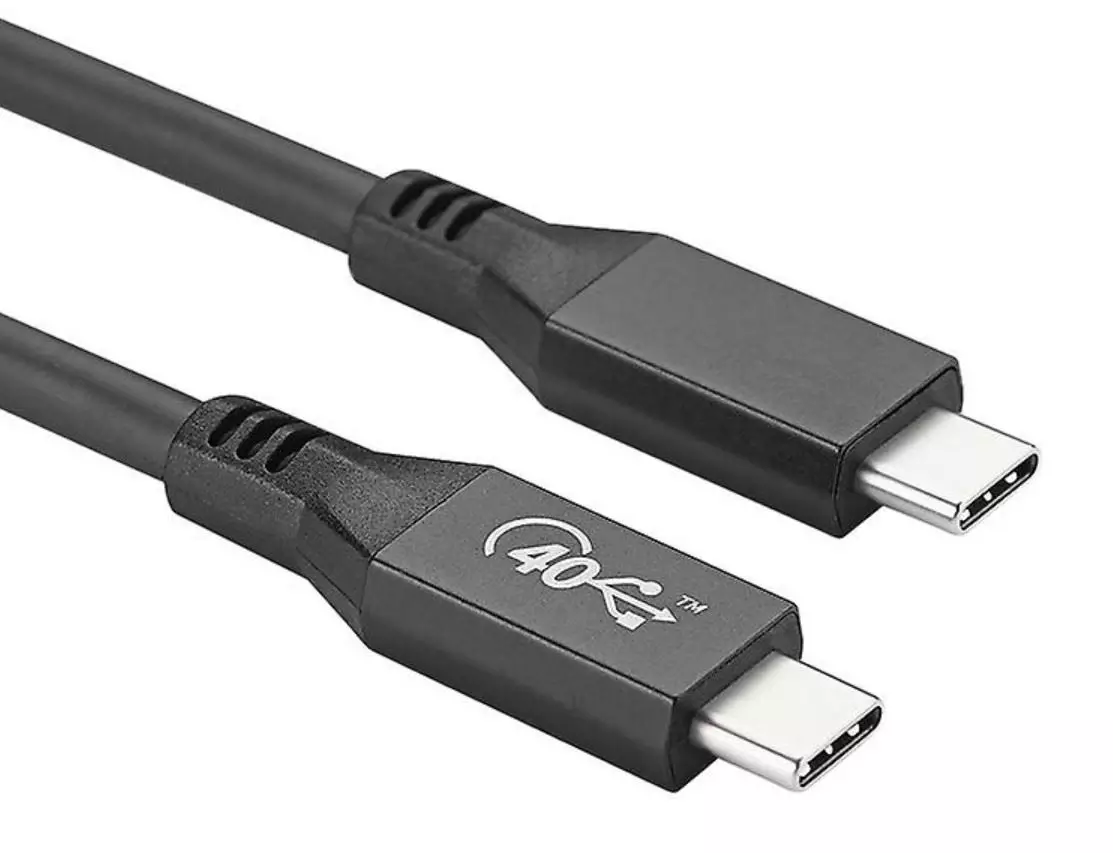
- USB C 20 Logo | USB 4.0 | 20 Gbps
- USB C 40 Logo | USB 4.0 | 40 Gbps | Thunderbolt 4 Enabled ONLY if carrying the Thunderbolt Logo
USB C Cable Wiring Examples:
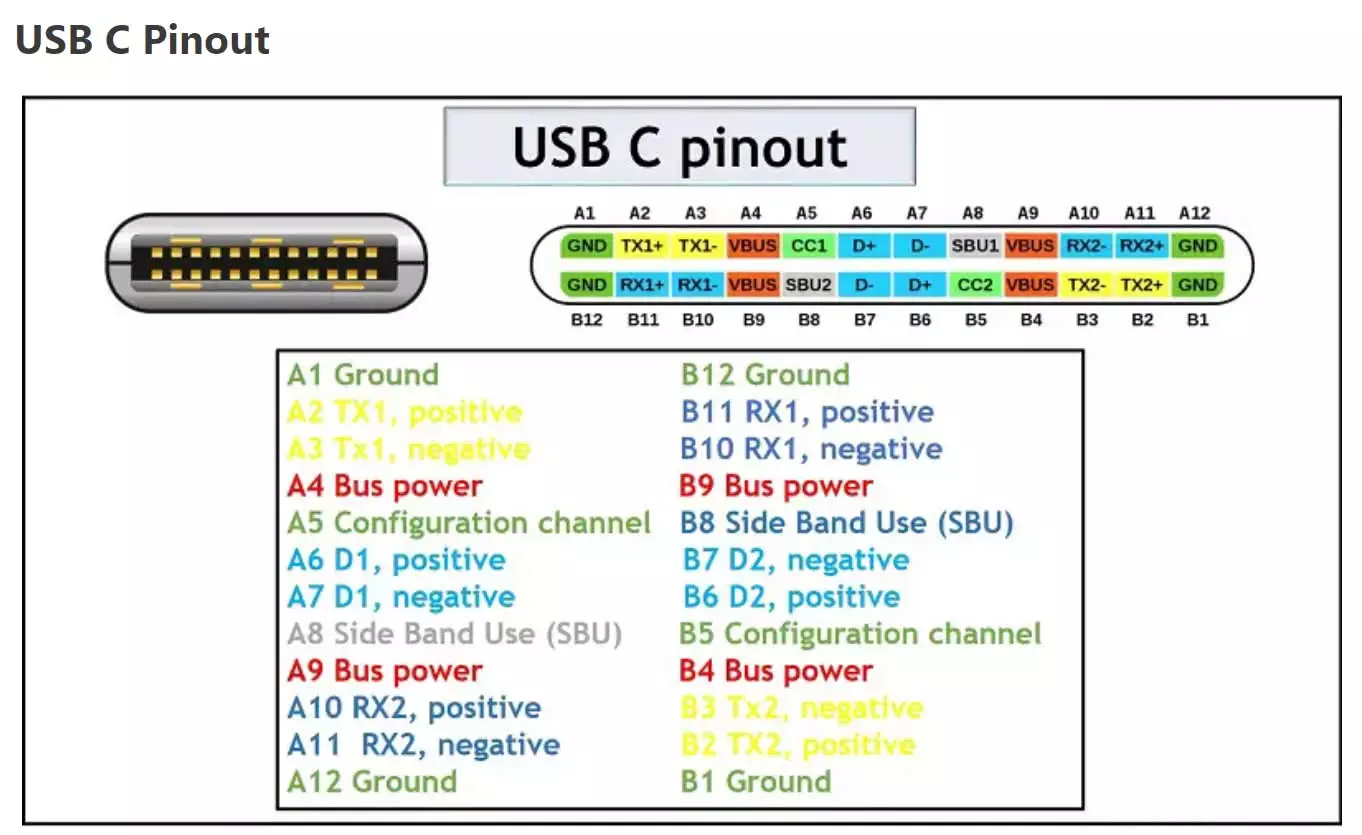
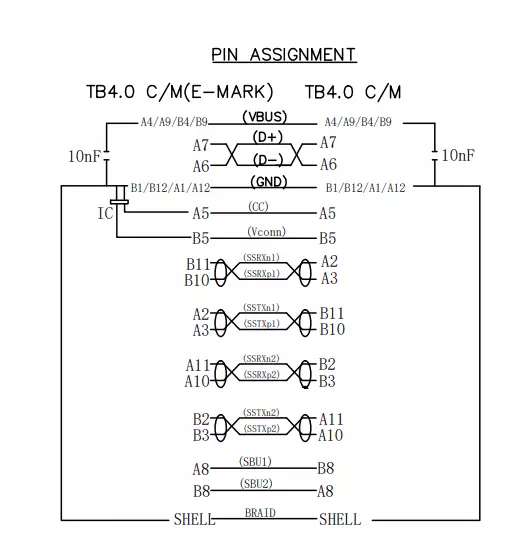
USB C is a 24-pin connector with a size of 8.4×2.6 mm. It is rectangular in shape with rounded edges. The pinout diagram of the USB C connector is shown in the figure below.
| Pin | Description | Pin | Description |
| A1 | Ground | B12 | Ground |
| A2 | Superspeed differential pair 1, TX, positive | B11 | Superspeed differential pair 2, RX, positive |
| A3 | Superspeed differential pair 1, TX, negative | B10 | Superspeed differential pair 2, RX, negative |
| A4 | Bus power | B9 | Bus power |
| A5 | Configuration channel | B8 | Side Band Use (SBU) |
| A6 | Differential pair 1, positive | B7 | Differential pair 2, negative |
| A7 | Differential pair 1, negative | B6 | Differential pair 2, positive |
| A8 | Side Band Use (SBU) | B5 | Configuration channel |
| A9 | Bus power | B4 | Bus power |
| A10 | Superspeed differential pair 4, RX, negative | B3 | Superspeed differential pair 3, TX, negative |
| A11 | Superspeed differential pair 4, RX, positive | B2 | Superspeed differential pair 3, TX, positive |
| A12 | Ground | B1 | Ground |
USB Type C Pin Description
Among the 24 pins, there are:
- two pairs of ground pins(GND)
- two pairs of power pins(VBUS)
- two differential pairs(D+ and D-)
- four shielded differential pairs(two sets of TX and RX).
- SBU and CC pins are two special-purpose pins in the connector.
VBUS and GND pins
One pair of GND pins are located at either end of the connector. VBUS pins allow power delivery with a voltage of up to 20V, but the default voltage of VBUS is 5V.
D+ and D- pins
D+ and D- pins are used from USB 2.0 standards for high-speed data transmission. There are two pairs of D+ and D- pins which are located at the center of the connector.
TX and RX pins
The two sets and TX and RX pins are meant for Enhanced Super Speed data transmission. Normally Charging ONLY Cheaper USB C Cables does not have these pins connected to save on wiring costs
CC / Channel Configuration Pins
The single pair of channel configuration pins handle the functions such as plug orientation detection, current advertisement, cable attachment, and removal detection and also manages the communication between Power Delivery and Alternate Mode.
SBU Pins
The SBU pair is used at low-speed signal paths while working in Alternate Mode.
The Alternate mode is an enhanced feature employed by USB 2.0. It incorporates third-party protocols like DisplayPort and HDMI using USB C.
No Logo or Cable USB Port no Color WHITE/BLACK -> Used in most Fast Charging, Supercharge, Adaptive Fast Charging Smartphone charging cables. Data Transfer speeds will be max around 42Mbps and these cables are not wired for optimal data speeds and structured for charging only. Although these cables below uses the USB Type A 2.0 spec ports and USB C Ports it is NOT wired for High Data speeds.

USB 3.2 Gen 1 Type A (5Gbps) to USB C SS 5Gbps to USB C Wiring
Blue Type A USB 3.0 Port. Data transfer speed will max out on the drive enclosure, solid state drive or m.2 nvme drive speed most of the time due to lowest speed supported by these cables which is 5Gbps.
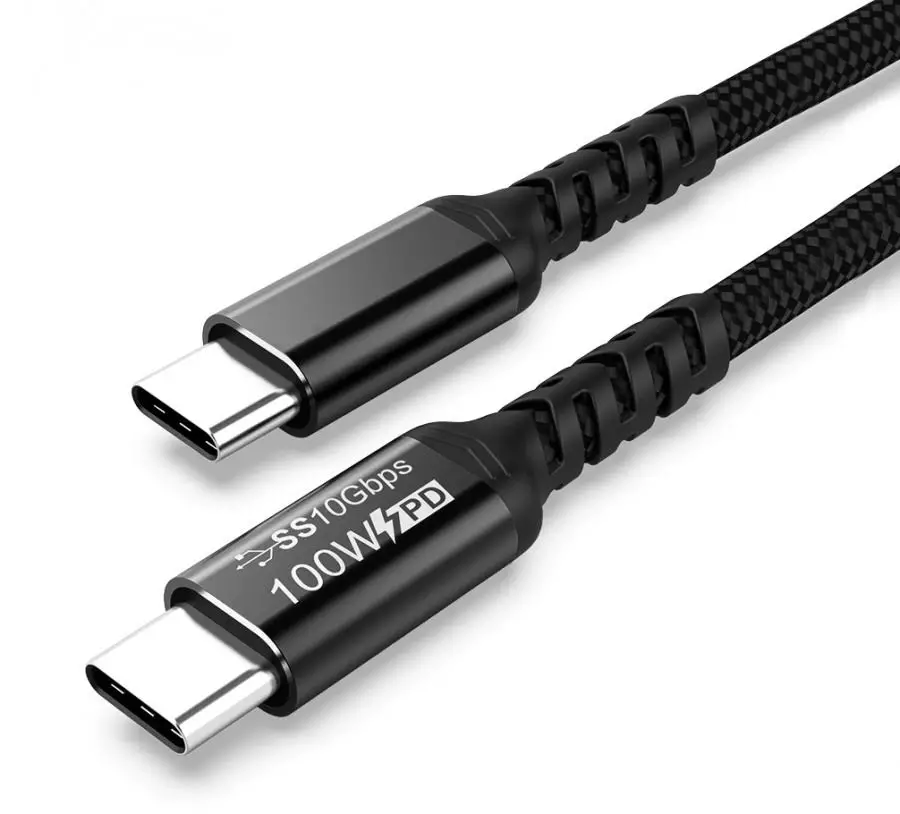
USB C 3.2 Gen 1.2 o USB C SS 10Gbps Cable
USB SS (SuperSpeed) 10Gbps indicated on Cable Head
USB 4.0 40Gbps USB C to USB C Cable (NOT Thunderbolt Certified since it does not have the Thunderbolt Logo)
USB SS (SuperSpeed) 40Gbps indicated on Cable Head
Thunderbolt 4 Certified Cable 40 Gbps, 4k 120hz –-> See Thunderbolt spec below
Intel Thunderbolt Specifications
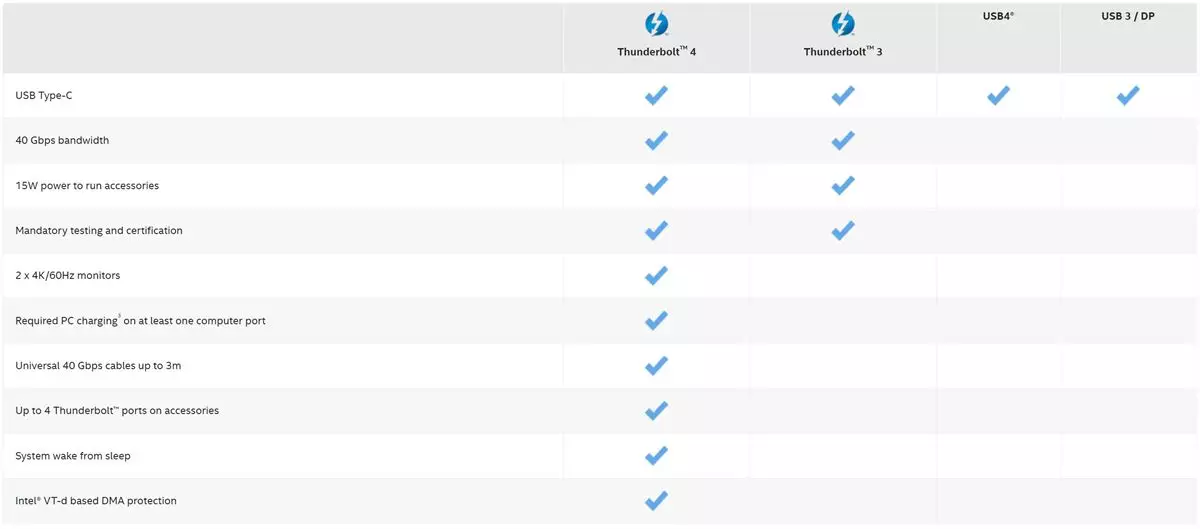
What is Thunderbolt 4?
Promoted by Intel as a universal connectivity experience, Thunderbolt 4 (TB4) is a “superset standard” incorporating USB4, DisplayPort and PCI Express (PCIe). In terms of performance, Thunderbolt 4 isn’t all that different from its predecessor. The big difference is that laptop, peripheral and cable makers must meet more stringent standards for Thunderbolt 4 certification so buyers can be confident that, at a minimum, they will get the following features:
- 40Gb/s data transfer speed over cables of up to 2 meters (6.5 feet) in length
- 32 Gb/s PCIe data transfer (twice that of Thunderbolt 3)
- Support for two 4K displays (or one 8K display)
- At least one port supporting 100W laptop charging
- Wake from sleep support
Intel’s Thunderbolt 3 controller halves power consumption and simultaneously drives two external 4K displays at 60 Hz (or a single external 4K display at 120 Hz, or a 5K display at 60 Hz. The controller supports PCIe 3.0 and other protocols, including DisplayPort 1.2 (allowing for 4K resolutions at 60 Hz).Thunderbolt 3 has up to 15 watts of power delivery on copper cables and no power delivery capability on optical cables. Using USB-C on copper cables, it can incorporate USB power delivery, allowing the ports to source or sink up to 100 watts of power. On most high end gaming motherboards the Intel Thunderbolt Function needs to be enabled in the Bios. For Thunderbolt to work BOTH the Port, USB C Cable AND the device needs to support it.
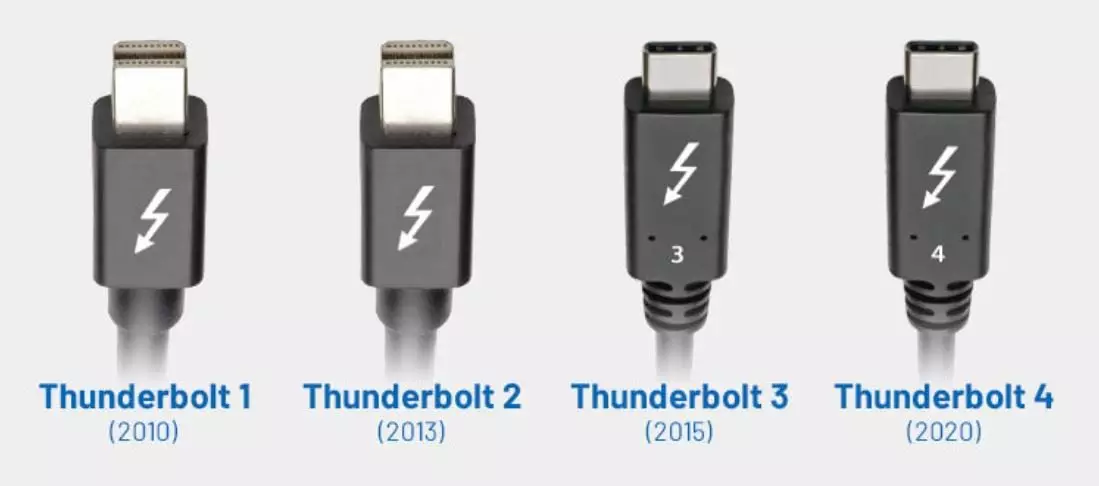
To see if a cable supports Intel Thunderbolt please check the Logo below and revision e.g TB3, TB4 etc of which Thunderbolt revision is supported. Thunderbolt 1 & 2 ports were mini-Displayport connectors but the Thunderbolt spec has moved to USB C connectors since Thunderbolt 3 Revision.
Thunderbolt Testing and Certification:
Despite Thunderbolt 4 products using the same USB Type-C connector as with USB 3, USB 4 etc —recognizable by its oval shape—Thunderbolt 4 brand certification requires higher minimum standards for power, data, and video, with constant 40 Gbps bandwidth in each direction and supports PCI Express (PCIe) connectivity for fast data transfer speed. Other USB-C cables, devices, and ports may be limited to a variable range of data speeds, with no guarantee of display quality nor simultaneous laptop charging. PCIe support is unavailable with USB 3 and optional on USB4. The Thunderbolt logo is a simple, sure-fire indicator of what a connection between devices can do.
Thunderbolt 4 USB C Connector Detailed Wiring Layout:
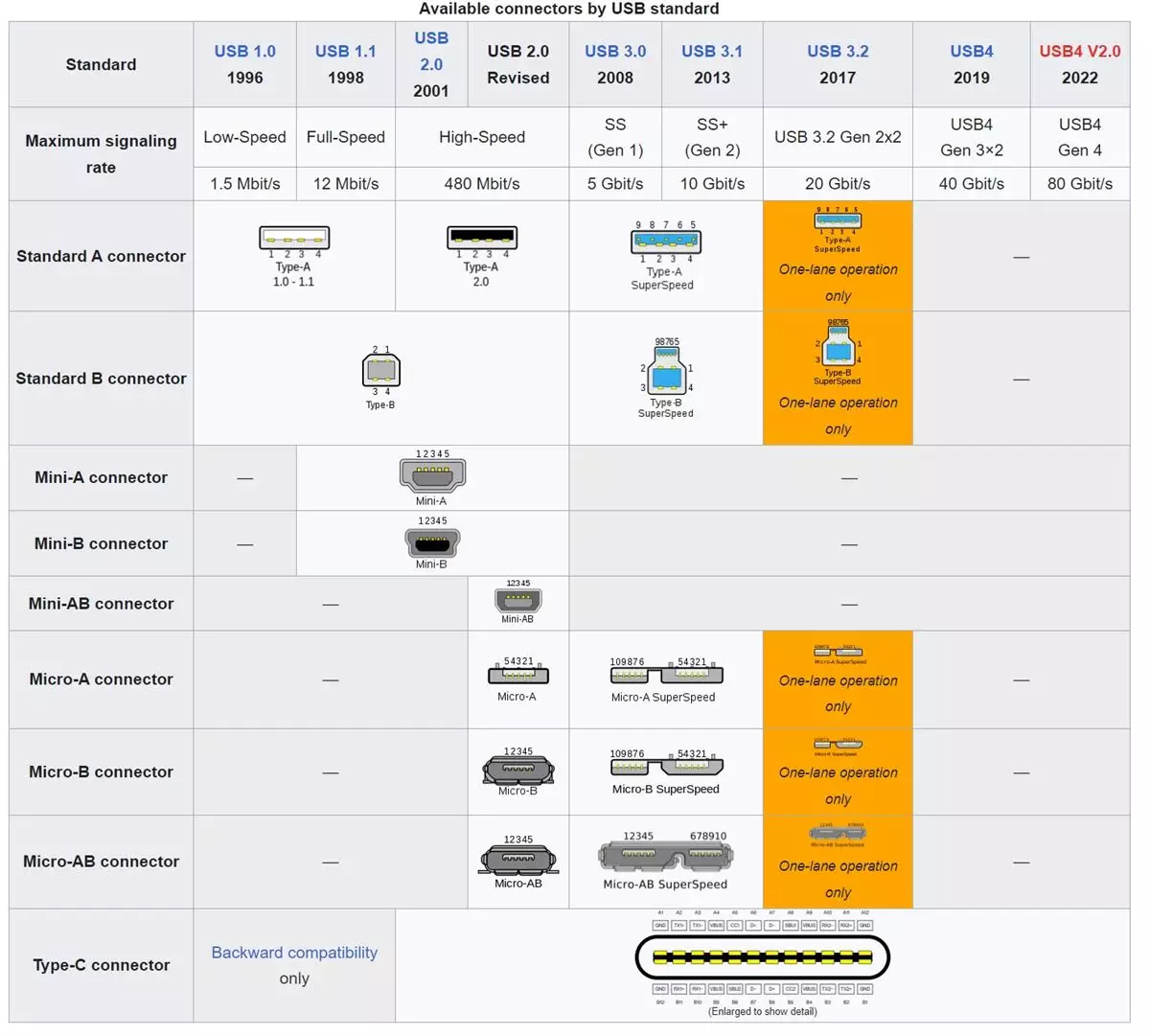
USB Connector Types | Type A, Type B, Type C, Mini A, Mini B, Micro A, Micro B